2월 CPI 발표! CPI와 주가 관계 + CPI 뜻, 금리, 인플레이션 한번에 정리!
목차
- 서론
- 소비자물가지수 (CPI)란?
- CPI와 인플레이션
- CPI와 주가 관계
- CPI와 기업 수익
- CPI와 금리
- CPI와 주식 시장의 반응
- 결론
1. 서론
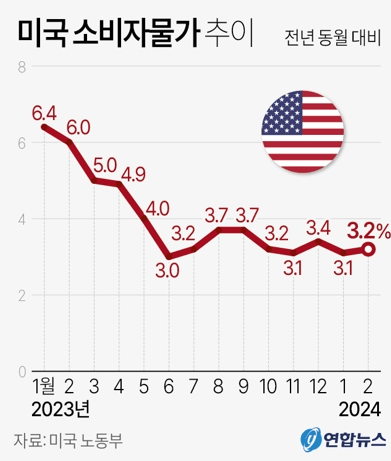
미 노동부가 2월 미국 소비자 물가지수(CPI)가 전년 동월 대비 3.2% 상승했다고 12일(현지시간) 발표했습니다. 한 달 전인 1월 소비자물가지수 상승률(3.1%) 대비 오른 데다 미 월스트리트저널이 집계한 전문가 예상치(3.1%)도 웃돌았습니다.
전월 대비 상승률은 0.4%로 1월(0.3%)보다 역시 상승률이 커졌습니다. 다만 전문가 예상치(0.4%)에는 부합했습니다. 변동성이 큰 에너지,식품을 제외한 근원CPI는 전년 동월 대비 3.8%, 전월 대비 0.4% 각각 상승해 모두 전문가 예상치를 0.1%포인트 웃돌았습니다.
소비자물가가 예상과 달리 높게 나타나면서 미 연준(Fed)가 예고하고 있는 금리 인하 시점이 당겨질 가능성은 희박하다는 해석이 나오고 있습니다. 현재 6월 또는 하반기에 금리를 인하할 것으로 점쳐지고 있으나 현재의 상황으로써는 이보다 더 늦어질 가능성도 있다는 추측입니다.
그렇다면 이번 포스팅에서는 소비자물가지수란 무엇인지 CPI 뜻 과 CPI와 인플레이션의 관계, CPI와 주가 관계 에 대해 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
2. 소비자물가지수 (CPI)란?
CPI는 소비자물가지수(Consumer Price Index)의 약자로, 특정 국가의 소비자들이 구매하는 상품과 서비스의 평균 가격 변화를 측정하는 지표입니다. 이것은 일반적으로 주요 소비 항목들의 가격 변동을 추적하여 경제의 인플레이션 수준을 평가하는 데 사용됩니다.
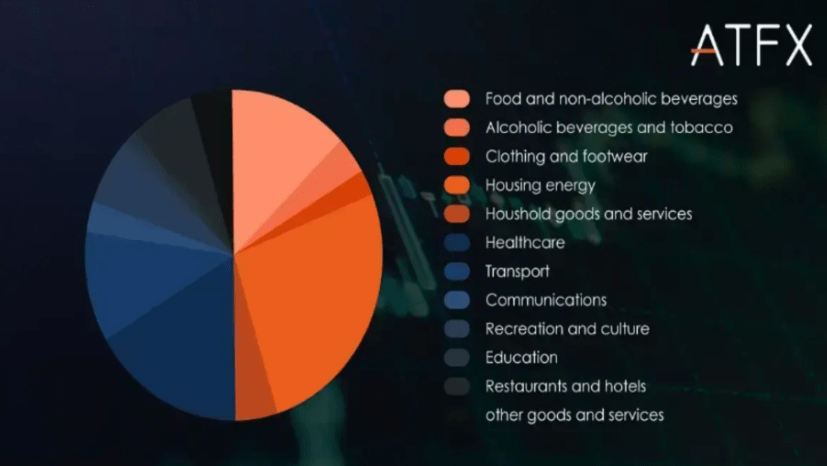
식자재, 교육, 에너지, 주거비용, 차량비용 등 수 많은 상품과 서비스 내용이 있는데, 이 중에서 몇가지 서비스 품목들의 물가가 어느 정도 상승했는지를 계산하여 수치로 나타낸 자료입니다.
CPI 구성요소에는 위와 같이 물가지수와 연관있는 품목들로 구성되어 있습니다. 이 중에서 주거를 나타내는 부동산 지표가 40% 이상 차지하고 있습니다. 우리나라도 현재 부동산 비중이 일반 소비에서 가장 많이 차지하고 있으며, 현재 우리나라의 경제 상태와 물가를 알 수 있는 가장 대표적인 항목입니다. 미국도 역시 부동산이 가장 큰 지표를 담당하고 있습니다. 그 다음으로는 식자재, 교통수단 등이 순차적으로 차지하고 있습니다.
위와 같은 구성요소들이 종합해서 CPI를 발표하게 되는데, 간혹 전반적인 수치는 내렸지만 한 구성의 수치가 급격하게 많이 오른다면, 이는 모든 전체 구성요소에 영향을 주기 때문에 전반적인 소비자물가지수는 오른 모습을 보이기도 합니다.
3. CPI와 인플레이션

CPI의 뜻을 아는 것은 한 나라의 경제 활동을 하는 주체로써 매우 중요합니다. CPI는 인플레이션을 측정하는 지표이기 때문입니다. 인플레이션은 일반적으로 물가 상승률을 나타냅니다. CPI는 소비자물가지수의 측정을 통해 이러한 인플레이션을 추적합니다. 이것은 소비자들이 상품과 서비스를 구매할 때 겪는 가격 변화를 나타내는 중요한 지표입니다.
인플레이션이란 물가는 상승하고 통화량의 증가로 화폐가치는 하락하는 것을 의미합니다. 즉, 내가 버는 돈으로 지금 무엇을, 얼마나 살 수 있는지 직접적으로 알 수 있습니다.
예를 들면, 월급은 그대로인데 소주가 3,000원에서 5,000원으로 올랐습니다.(CPI 상승) 소주가 비싸지자 사람들의 소비가 줄고, 같은 3,000원으로 소주를 살 수 없게 되자 예전의 3,000원보다 지금의 3,000원의 가치가 떨어졌다고 판단합니다.(화폐가치 하락)
이렇게 인플레이션이 발생하게 됩니다.
4. CPI와 주가 관계

CPI와 주가 관계 는 아주 밀접합니다. 뿐만 아니라 금리 인상 혹은 금리 인하, 인플레이션 등 모든 요소들이 서로 영향을 끼치는 관계입니다. CPI <-> 금리 <-> 인플레이션 <-> 주가 이렇게 나열할 수 있습니다.
그렇다면 CPI가 주가에 어떻게 영향을 미치는지 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
4.1 CPI와 기업 수익
CPI가 상승하면 기업의 생산 비용도 증가하게 됩니다. 원자재나 노동비용이 증가하면 기업이 그 비용을 제품 가격으로 전가할 가능성이 있습니다. 또한 위에서 말씀드렸던 예시를 다시 사용해서 예를 들자면, 소주가 CPI 상승으로 인한 원자재 상승으로 3,000원 -> 5,000원으로 가격이 오르면 시민들의 소주 소비는 급격하게 줄 수밖에 없습니다. 월급은 그대로인데 소주 값이 오르니 소비를 줄일 수 밖에 없게 됩니다.
그렇게 되면 소주를 판매하는 기업의 수익도 줄어들게 됩니다. 기업의 수익은 그 기업의 주가에 엄청난 영향을 미칩니다. 기업의 실적이 좋지 않으면 주가는 하락하고, 기업의 실적이 좋으면 주가는 상승하게 됩니다.
이렇게 기업의 실적은 연결되어 있는 회사와도 전반적인 영향을 끼치기 때문에 도미노처럼 줄줄이 기업의 실적이 하락하게 됩니다. 이렇기 때문에 CPI는 인플레이션에 영향을 주고 인플레이션은 기업의 주가에 영향을 줄 수 밖에 없습니다.
4.2 CPI와 금리
CPI가 주가에 영향을 끼치는 또 한가지 이유는 바로 금리 변동 가능성입니다. 인플레이션이 높아지면 중앙은행은 물가를 바로 잡기 위해서 금리를 인상해 더 이상 높아지지 않게 방어를 하고, 반대로 낮은 인플레이션은 경기 침체를 막기 위해 금리를 인하해 돈을 쓰게 해서 경제를 활성화 하고자 합니다. 이것이 중앙은행의 역할이기도 합니다.
기업들에게는 부채라는 것이 존재합니다. 사업확장을 위해 은행에서 돈을 빌리는 행위를 말합니다. 하지만 이 금리라는 것은 변동성이 있기 때문에 은행에 내야하는 이자가 달라지게 됩니다. 즉, 금리가 올라가면 대출 비용(이자 비용)이 증가하기 때문에 기업의 이익이 감소하게 됩니다. 위에서 언급 드렸던 것처럼 기업의 이익은 주가에 영향을 미치기 때문에 금리가 상승할 때는 기업의 이익이 줄기 때문에 주가는 떨어지게 됩니다. 반대로 금리가 인하하면 기업의 이익은 상승하기 때문에 주가도 상승하게 됩니다.
금리는 투자자들의 투자심리에도 많은 영향을 미칩니다. 금리가 오른다면 투자자들은 변동이 심하고 손해를 볼 수 있는 주식 시장에서 안전한 은행 금리 상품으로 눈을 돌리게 됩니다. 예를 들면 금리가 올라서 은행에서 1년에 이자 5% 짜리 금리가 나온다면 투자자들은 금리가 올라 실적이 감소된 기업의 주식을 들고 있어도 5%의 수익을 기대 할 수 없기 때문에 더 오르진 않지만 최소 5%의 수익을 얻을 수 있는 은행 상품에 투자하게 됩니다.
이러한 심리는 결국 기업의 주가가 하락하는 이유가 됩니다.
4.3 CPI와 주식 시장의 반응
CPI가 예상보다 높게 나오면 시장은 인플레이션 압력이 높아지고 경기가 둔화될 것으로 예상하여 주식 시장이 부정적으로 반응할 수 있습니다. 그러나 경우에 따라서는 기업이 가격 인상을 통해 수익을 보호할 수 있으므로, CPI 상승이 주가에 직접적으로 부정적인 영향을 미치는 것은 아닙니다.
5. 결론
CPI는 주가에 영향을 미치는 요인 중 하나이지만, 이것은 다른 요인들과 함께 고려되어야 합니다. CPI의 변화는 경제의 건강 상태를 반영할 수 있지만, 주가는 더 복잡한 요인들에 의해 영향을 받으므로 단독으로 해석할 때는 주의가 필요합니다. 그럼에도 CPI의 뜻과 이해는 반드시 필요합니다.

February CPI Release! Understanding the Relationship Between CPI and Stock Prices, Plus Definitions, Interest Rates, and Inflation
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
- CPI and Inflation
- Relationship between CPI and Stock Prices
- 4.1 CPI and Corporate Profits
- 4.2 CPI and Interest Rates
- 4.3 CPI and Stock Market Reaction
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
The U.S. Department of Labor announced on the 12th (local time) that the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for February rose by 3.2% compared to the same month last year. This figure surpassed both the January CPI increase rate (3.1%) and the expert consensus (3.1%) compiled by The Wall Street Journal.
The month-on-month increase rate also rose to 0.4%, up from January (0.3%). However, it aligned with the expert forecast (0.4%). Excluding volatile energy and food, the core CPI rose by 3.8% year-on-year and 0.4% month-on-month, both surpassing expert expectations by 0.1 percentage points.
With consumer prices unexpectedly high, there are interpretations suggesting that the possibility of the Federal Reserve (Fed) implementing rate cuts as announced may diminish. While a rate cut is expected in June or the second half of the year, there is speculation that it could be delayed further given the current situation.
In this post, we will explore what the Consumer Price Index (CPI) means, its relationship with inflation, and its impact on stock prices.
2. What is the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
CPI stands for Consumer Price Index, a measure of the average price change of goods and services purchased by consumers in a specific country. It is typically used to evaluate the level of inflation in the economy by tracking the price fluctuations of major consumer items.
There are various components that constitute CPI, including food, education, energy, housing costs, and transportation expenses. Among these, housing-related indicators account for more than 40%. Housing also plays a significant role in the South Korean economy, and it is the most representative item for understanding the economic situation and prices. Similarly, housing is a major component in the United States. Following housing, food and transportation expenses are sequentially significant.
The CPI is calculated by aggregating these components to provide a numerical representation of price changes. Occasionally, even if the overall figure decreases, a sharp increase in one component may affect all other components, resulting in an overall increase in the Consumer Price Index.
3. CPI and Inflation
Understanding the meaning of CPI is crucial as it is an indicator of inflation. Inflation generally refers to the increase in prices and the decrease in the purchasing power of money due to the increase in the money supply. In other words, it directly reflects how much one can buy with the money they earn.
For example, if the price of a bottle of soju rises from 3,000 won to 5,000 won due to CPI increases, consumers may reduce their consumption as they cannot afford to buy as much soju with the same amount of money. As a result, the value of 3,000 won compared to before has decreased. This is known as a decrease in the purchasing power of money.
This is how inflation occurs.
4. Relationship between CPI and Stock Prices
4.1 CPI and Corporate Profits
When CPI rises, the production costs of companies also increase. If the prices of raw materials or labor costs increase, companies may pass on these costs to product prices. Using the example mentioned earlier, if the price of soju rises from 3,000 won to 5,000 won due to CPI increases in raw materials, consumers’ consumption of soju may sharply decrease. Since the salary remains the same but the price of soju increases, consumers will have to reduce their consumption.
As a result, the profits of companies selling soju will also decrease. Company profits have a significant impact on stock prices. If a company’s performance is poor, the stock price will fall, and if a company’s performance is good, the stock price will rise.
Company performance is linked to other companies, so a decrease in company performance causes a domino effect. Therefore, CPI affects inflation, which in turn affects company stock prices.
4.2 CPI and Interest Rates
Another reason CPI affects stock prices is the possibility of interest rate fluctuations. When inflation rises, central banks may raise interest rates to control inflation and prevent further increases. Conversely, low inflation prompts central banks to cut interest rates to stimulate spending and economic activity. This is also the role of central banks.
Companies have debts for business expansion, borrowing money from banks. However, interest rates fluctuate, so the interest owed to the bank changes. If interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing (interest costs) for companies increases, leading to a decrease in profits. As mentioned earlier, company profits have an impact on stock prices. When interest rates rise, company profits decrease, and stock prices fall. Conversely, when interest rates are reduced, company profits increase, and stock prices rise.
Interest rates also affect investors’ sentiment. If interest rates rise, investors may shift their focus from volatile and potentially loss-making stock markets to safer bank interest products. For example, if interest rates rise and a 5% interest rate product is available at a bank, investors may invest in bank products where they can expect at least a 5% return, even if they hold shares of a company whose performance has declined due to rising interest rates.
This psychological aspect ultimately leads to a decrease in stock prices.
4.3 CPI and Stock Market Reaction
If CPI exceeds expectations, the market may anticipate increased inflationary pressures and economic slowdown, resulting in a negative response in the stock market. However, depending on the circumstances, if companies can protect their profits through price increases, the impact of CPI increases on stock prices may not be direct.
5. Conclusion
While CPI is one of the factors affecting stock prices, it should be considered along with other factors. Changes in CPI reflect the health of the economy, but stock prices are influenced by more complex factors, requiring careful interpretation. Nevertheless, understanding the meaning of CPI is essential.