목차
- 소개
- 가계 자산 감소의 원인: 부동산 하락
- 2.1 자산 감소의 배경
- 2.2 부동산 자산 감소
- 부동산 하락의 원인: 기준금리 인상과 물가 상승
- 3.1 기준금리 인상의 영향
- 3.2 물가 상승과 주택 거래 감소
- 부동산 하락으로 인한 자산 감소의 영향
- 4.1 가구 평균 자산 감소
- 4.2 부채와 금융부채의 변화
- 부동산 자산의 압도적 비중과 영향
- 5.1 부동산 자산의 비중 변화
- 5.2 부동산 자산의 하락과 가구 자산 감소
1. 소개
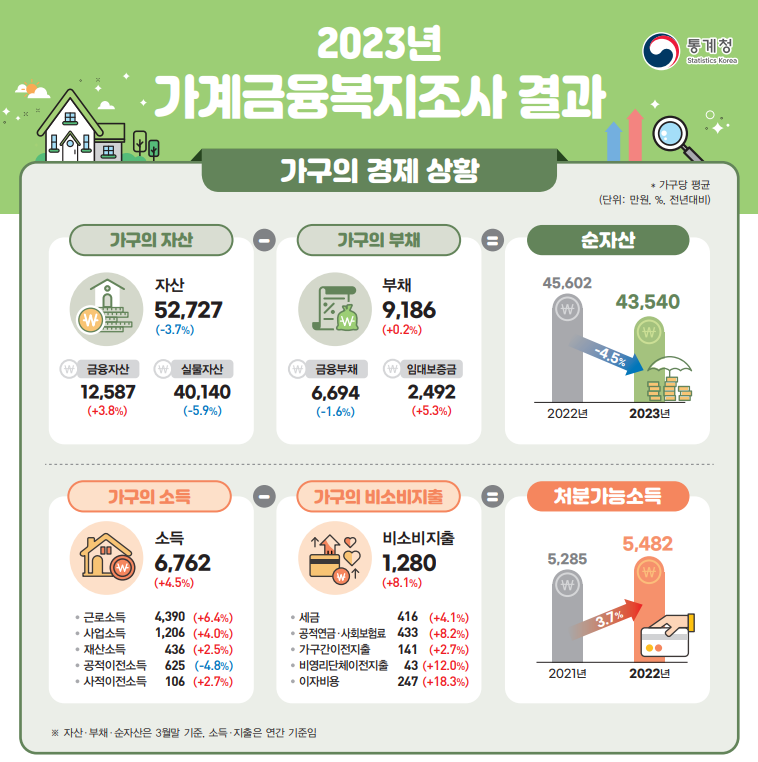
2023년 가계금융복지조사 결과에 따르면, 한국 국민의 자산 규모가 처음으로 감소했다. 이 감소의 주된 이유는 부동산 가격의 하락에 있었다.
2. 가계 자산 감소의 원인: 부동산 하락
2.1 자산 감소의 배경
국내 가구당 평균 자산은 전년 대비 3.7% 감소한 5억 2727만원으로 나타났다. 부동산 자산이 75%를 차지하다보니 집값의 등락이 가구 자산 규모에 큰 영향을 미쳤다.
2.2 부동산 자산 감소
부동산 자산은 전년 대비 6.6% 축소된 3억 7677만원으로 나타났다. 지난해 집값 하락은 기준금리 인상으로 대출 이자 부담이 증가하면서 주택 거래가 감소하고 집값이 하락한 결과로 나타났다.
3. 부동산 하락의 원인: 기준금리 인상과 물가 상승
3.1 기준금리 인상의 영향
금리 인상으로 대출 이자 부담이 커져 주택 거래가 감소하면서 집값이 내려갔다. 물가 상승을 잡기 위해 한국은행이 기준금리를 높여야 했던 상황에서 발생한 현상이다.
3.2 물가 상승과 주택 거래 감소
물가 상승으로 기준금리를 높여야 했고, 이로 인해 대출 감소와 함께 주택 거래가 줄면서 집값이 하락한 흐름이 발생했다.
4. 부동산 하락으로 인한 자산 감소의 영향
4.1 가구 평균 자산 감소
집값 하락의 여파로 가구의 자산에서 부채를 뺀 ‘순자산’도 4억 3540만원으로 1년 전보다 4.5% 감소했다.
4.2 부채와 금융부채의 변화
가구의 평균 부채는 전년 대비 0.2% 증가한 9186만원으로 나타났다. 금융부채는 대출 금리 상승으로 1.6% 감소하였으며, 금리 인상으로 대출 금리가 높아지면서 금융부채가 축소되었다.
5. 부동산 자산의 압도적 비중과 영향
5.1 부동산 자산의 비중 변화
부동산 자산의 비중은 2021년 73.7%에서 71.5%로 2.2% 포인트 감소했다.
5.2 부동산 자산의 하락과 가구 자산 감소
부동산 자산의 하락은 전체 자산 규모 감소를 이끌었는데, 부동산 자산이 전체 자산에서 차지하는 비중이 크기 때문에 가구 자산이 처음으로 감소한 것으로 나타났다.
결론
이번 조사에서 나타난 결과는 부동산 자산의 하락이 국민의 가계 자산에 큰 영향을 미쳤음을 보여준다. 부동산 가격의 하락은 기준금리 인상과 물가 상승에 따른 대출 감소와 집값 하락으로 이어져 국민의 자산 규모를 줄였다. 가구의 부채 역시 대출 이자 부담의 증가로 인해 높아졌으며, 이로 인해 주택 거래가 감소하고 집값이 하락하는 현상이 나타났다. 이러한 결과는 부동산이 국민의 자산 구성에서 중요한 비중을 차지하고 있음을 보여주며, 부동산 시장의 안정성이 국민 경제에 미치는 영향을 강조한다.
Reasons for the Decrease in South Korean National Assets and Real Estate Price Decline in 2023
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Causes of Decrease in Household Assets: Decline in Real Estate
- 2.1 Background of Asset Reduction
- 2.2 Decrease in Real Estate Assets
- Reasons for Real Estate Decline: Base Rate Increase and Inflation
- 3.1 Impact of Base Rate Increase
- 3.2 Inflation and Decrease in Real Estate Transactions
- Impact of Real Estate Decline on Asset Reduction
- 4.1 Decrease in Average Household Assets
- 4.2 Changes in Debt and Financial Debt
- Overwhelming Proportion of Real Estate Assets and its Influence
- 5.1 Changes in the Proportion of Real Estate Assets
- 5.2 Decline in Real Estate Assets and Reduction in Household Assets
1. Introduction
The results of the 2023 Household Financial Welfare Survey reveal a notable decrease in the financial assets of South Korean citizens, marking the first reduction since the compilation of relevant statistics began in 2012. The primary cause behind this decline can be attributed to the fall in real estate prices.
2. Causes of Decrease in Household Assets: Decline in Real Estate
2.1 Background of Asset Reduction
As of March 2023, the average per-household assets in South Korea decreased by 3.7%, amounting to KRW 527.27 million. Given that real estate assets constitute approximately 75% of total assets, fluctuations in property values had a substantial impact on household asset sizes.
2.2 Decrease in Real Estate Assets
Real estate assets experienced a significant contraction, dropping by 6.6% to KRW 376.77 million from the previous year’s KRW 435.5 million. The decrease in real estate assets played a pivotal role in the overall reduction of household assets.
3. Reasons for Real Estate Decline: Base Rate Increase and Inflation
3.1 Impact of Base Rate Increase
The increase in base interest rates led to a surge in the burden of loan interest payments, resulting in a reduction in housing transactions and subsequent depreciation in property values. The Bank of Korea had no choice but to raise the base interest rate due to rising inflation, reaching 6.3% year-on-year in July of the previous year, the highest level in 24 years since the 6.8% during the foreign exchange crisis in November 1998.
3.2 Inflation and Decrease in Real Estate Transactions
The increase in inflation necessitated a rise in the base interest rate. Consequently, heightened loan interest burdens led to a decrease in housing transactions, contributing to the decline in property values. The flow of events followed: ‘Inflation → Base Rate Increase → Decrease in Loans → Decline in Housing Transactions → Drop in Property Values.’
4. Impact of Real Estate Decline on Asset Reduction
4.1 Decrease in Average Household Assets
As a result of the ripple effects of falling property values, the ‘net assets’—assets minus debts—of households decreased by 4.5%, amounting to KRW 435.4 million compared to the previous year.
4.2 Changes in Debt and Financial Debt
The average debt per household increased marginally by 0.2% to KRW 91.86 million. Financial debts, including mortgage and credit loans, decreased by 1.6%, while rental security deposits increased by 5.3%. The rise in loan interest rates contributed to the reduction in financial debts.
5. Overwhelming Proportion of Real Estate Assets and its Influence
5.1 Changes in the Proportion of Real Estate Assets
The proportion of real estate assets decreased from 73.7% in 2021 to 71.5% in the previous year, marking a 2.2% decrease.
5.2 Decline in Real Estate Assets and Reduction in Household Assets
The decline in real estate assets became a driving force for the reduction in overall asset sizes. The overwhelming weight of real estate assets in the entire portfolio of household assets is evident, contributing to the first recorded decrease in household assets.
Conclusion
The survey results underscore the significant impact of the decline in real estate assets on the financial well-being of South Korean households. The reduction in property values, driven by the increase in base interest rates and inflation, resulted in a contraction of national assets. The prominence of real estate in the composition of household assets highlights the importance of real estate market stability on the overall economy.